Benzodiazepine withdrawal refers to the process when someone who has been taking benzos, often prescribed for sleep or anxiety disorders, stops or reduces their dosage. This cessation can lead to a range of physical and psychological symptoms as the body adjusts to the absence of the drug.
The withdrawal from benzodiazepines happens in stages, each with its own set of symptoms and duration. In this article, we will explore the withdrawal timeline and the phases individuals may experience as they navigate the process.
Key Takeaways
Benzodiazepine withdrawal occurs when a person stops or reduces the dosage of these medications. Here’s what you need to know:
- Withdrawal from benzodiazepine unfolds in stages, each with its unique challenges and durations.
- Various factors play a part in the varying duration and severity of symptoms of benzo withdrawal.
- Management of withdrawal involves different approaches, such as medication-assisted treatment (MAT).
For those struggling with benzodiazepine dependence, there is hope for a better future. Contact The Recovery Team at (800) 817-1247.
Understanding Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
Benzodiazepines are a class of psychoactive drugs commonly prescribed for medical conditions such as anxiety, insomnia, and seizure disorders. Examples include medications like diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), and alprazolam (Xanax).
While they can be effective in managing certain medical conditions, long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to physical dependence, and sudden cessation or a rapid reduction in dosage can result in withdrawal symptoms.
Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms can vary widely in severity and duration depending on different factors. Here are the most common benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms:
- Anxiety and Panic: Heightened feelings of anxiety, panic attacks, and restlessness are common during withdrawal.
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep is a common withdrawal symptom.
- Tremors and Muscle Twitching: Physical symptoms such as tremors and muscle twitching may occur.
- Irritability and Mood Swings: Emotional volatility and mood changes are typical during withdrawal.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting, can be present.
- Sweating: Increased sweating, especially at night, is a common withdrawal symptom.
- Headaches: Headaches and migraines may occur during benzodiazepine withdrawal.
- Sensory Disturbances: Sensitivity to light, sound, and touch may increase. Some people might experience tingling sensations or heightened perception.
- Depersonalization and Derealization: Some individuals may experience feelings of detachment from themselves or their surroundings.
In severe cases, benzo withdrawal can lead to seizures or a condition called delirium tremens, characterized by confusion and hallucinations and, in extreme cases, can be life-threatening.
Therefore, it’s crucial for individuals withdrawing from benzodiazepines to do so under medical supervision. Tapering off the medication gradually under a doctor’s guidance is generally the safest approach.
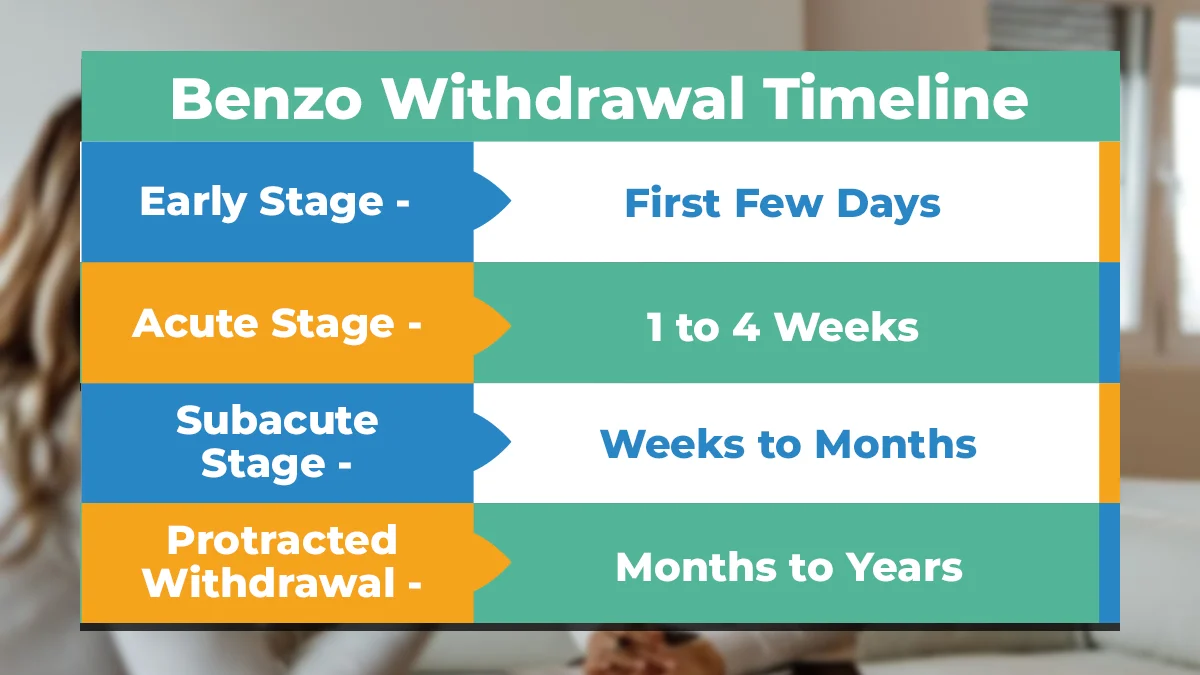
Timeline of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal
The withdrawal timeline for benzodiazepines can vary significantly among individuals depending on various factors. However, here’s a general breakdown of the possible phases:
Early Stage (First Few Days)
In the early stage of benzodiazepine withdrawal, which typically begins within a few hours to days after stopping the medication, mild symptoms emerge. These can include heightened anxiety, restlessness, trouble sleeping, and irritability.
Physical symptoms might surface, such as headaches, sweating, and palpitations. These initial experiences vary in intensity among individuals but often reflect the body adjusting to the absence of the drug.
Acute Stage (1 to 4 Weeks)
Moving into the acute stage, which usually occurs within the first week and lasts up to a month, symptoms intensify. Symptoms of anxiety can escalate, along with panic attacks and increased heart rate.
Physical symptoms, like muscle aches or tremors, might persist or worsen. Insomnia and mood swings might also be pronounced during this phase, making it challenging for individuals to cope with daily activities.
Subacute Stage (Weeks to Months)
The subacute stage occurs after the acute phase, typically within a month to several months post-discontinuation. While the acute symptoms start to diminish, some lingering effects persist.
Mood disturbances, such as depression or irritability, may persist, albeit less intensely. Individuals might continue to experience intermittent anxiety, trouble sleeping, and cognitive difficulties, although these symptoms gradually ease over time.
Protracted Withdrawal (Months to Years)
Sometimes, a protracted withdrawal phase follows, extending beyond the typical timeline. This stage can be unpredictable, with intermittent resurgence of withdrawal symptoms even after several months or years post-cessation.
Symptoms may vary greatly between individuals, including occasional bouts of anxiety, insomnia, mood swings, or cognitive issues. While less common, some individuals may experience prolonged and intermittent symptoms that persist for an extended period.
Withdrawal Timeline Variables
The withdrawal timeline for benzos can vary widely from person to person. Here are some factors that can affect the benzodiazepine withdrawal timeline:
Duration of Use
The length of time someone has been taking benzodiazepines plays a significant role in withdrawal. Those who use these medications for a longer duration face a more extended withdrawal process compared to those who use them for shorter periods.
Dose
The amount of benzodiazepine medication taken daily also affects withdrawal. Higher doses of benzos usually lead to more severe withdrawal symptoms. People taking high doses may experience more intense and prolonged withdrawal periods.
Type of Benzodiazepine Used
Different benzodiazepines have varying strengths and durations. Short-acting benzodiazepines like Xanax might result in faster onset but quicker withdrawal, while long-acting benzos like Valium might lead to a more prolonged withdrawal process.
Individual Physiology
Each person’s body responds uniquely to medication. Factors like metabolism, genetics, overall health, and tolerance levels influence how quickly someone experiences withdrawal symptoms and how long they last.
Dependency Level
The level of dependence on benzodiazepines impacts withdrawal. Those with higher levels of dependency are likely to experience more intense withdrawal symptoms and an extended timeline for recovery.
Tapering Method
The approach used to stop benzodiazepine intake matters. Gradual tapering, where the dosage is slowly reduced under medical guidance, can help manage withdrawal symptoms and shorten the timeline.
Psychological Factors
Mental health and psychological factors can influence withdrawal. Anxiety, stress, or other mental health disorders can exacerbate withdrawal symptoms and prolong the timeline.
Co-occurring Conditions
Having other health conditions alongside benzodiazepine use can impact withdrawal. Conditions like chronic pain, substance use disorders (SUDs), or psychiatric illnesses may complicate the withdrawal process, extending the timeline.
These factors collectively shape the benzodiazepine withdrawal experience, impacting the duration, severity, and challenges individuals face during this period.
Managing Benzodiazepine Withdrawal: Effective Approaches
Managing benzodiazepine withdrawal is a complex process that often requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. Here are some strategies that are commonly used to manage benzo withdrawal symptoms:
Medical Detox Program
Entering a medical detox program is often the initial step in managing benzodiazepine withdrawal. This supervised setting, usually within a hospital or specialized treatment facility, provides 24/7 medical care. Trained professionals monitor individuals during the withdrawal process, ensuring safety and comfort.
Benzo detox helps manage severe symptoms of withdrawal and allows for a more gradual tapering of the medication under professional guidance. This structured approach aims to minimize risks and complications associated with abrupt withdrawal.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) involves the use of specific medications to ease withdrawal symptoms and support the recovery process. Doctors may prescribe longer-acting benzodiazepines, like diazepam, and gradually reduce the dosage to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Other medications, like certain antidepressants or anticonvulsants, can also aid in managing symptoms during withdrawal. Medical professionals often supervise MAT to ensure a safe and effective withdrawal.
Counseling and Behavioral Therapies
Counseling and behavioral therapies play a pivotal role in managing benzodiazepine withdrawal. These approaches involve talking with trained professionals who help individuals navigate through the emotional and psychological aspects of withdrawal.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps equip individuals with coping mechanisms to handle triggers, manage stress, and address root causes contributing to benzodiazepine use. Individual and group therapy sessions can provide vital support and guidance throughout the withdrawal journey.
Holistic and Lifestyle Approaches
Holistic and lifestyle approaches encompass various techniques that support overall well-being during benzodiazepine withdrawal. These include mindfulness practices, meditation, yoga, and relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote a sense of calmness.
Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and ensuring adequate sleep are vital components of holistic approaches. Support groups and peer networks offer valuable emotional support and encouragement throughout recovery.
The Recovery Team: Your Journey, Our Commitment
At The Recovery Team, we’re here to guide your journey with our comprehensive care options, including inpatient rehab and outpatient care.
Our programs are designed with you in mind, offering a range of options tailored to your needs. From personalized therapy sessions to expert medication management and holistic approaches, we have the tools to support you on your journey to lasting recovery.
If you’re dealing with both addiction and mental health issues, our dual diagnosis program is specifically crafted to address both challenges together.
Call (800) 817-1247 to speak to a member of our team.